The Ultimate NFT Guide : How Make NFT Collection For Beginners
Updated 07 Aug 2022

Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have gotten a lot of attention lately. This isn’t surprising, especially when you hear stories about artists who have made tens of millions of dollars selling a single NFT. In this comprehensive Guide, we will share with you how to create your first NFT collection from zero to one and how exactly to sell and mint your NFTs even if you don’t have any coding or programming skills. This step-by-step guide is for both beginners who don’t have any idea of what it is NFT, and for pros who are searching for the best and easiest NFT generator to make and sell their NFT project.
Make NFT Collection from scratch for BeginnersVocabulary summary
NFTs
Non-Fungible Tokens, An NFT is a digital asset that represents real-world objects like art, music, in-game items, and videos. They are created, bought, and sold online, frequently with cryptocurrency, and they are generally encoded with the same underlying software as many cryptos.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT NFTs:
- NFTs are unique cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain and cannot be replicated.
- NFTs can represent real-world items like artwork and real estate.
- "Tokenizing" these real-world tangible assets makes buying, selling, and trading them more efficient while reducing the probability of fraud.
- NFTs can also function to represent individuals' identities, property rights, and more.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system.
A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain. Each block in the chain contains a number of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger. The decentralized database managed by multiple participants is known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Blockchain is a type of DLT in which transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash.

Ethereum: It comes in second place after Bitcoin and is one of the most favored blockchain platforms for creating decentralized applications. Ethereum has been responsible for creating an open economy by providing its own cryptocurrency and platform for developing decentralized applications. The platform can be accessed by anyone regardless of location and background. There is a dominance of Ethereum when it comes to the market of digital collectibles as it has been the first platform that provided a way for NFTs.
Solana: It is undoubtedly a great competitor to Ethereum. The platform has been created to provide developers with a place to develop user-oriented applications. The most intriguing feature of the platform is its efficiency. Solana is known to process around 50,000 to 65,000 transactions every second, making it one of the fastest blockchain platforms available. It is currently the quickest blockchain platform available to developers for creating scalable applications and due to this, it has the most efficient ecosystem.
Polygon: It is one of the most renowned digital blockchain platforms available to users. The platform is responsible for providing digital assets and economies. The major functionality of Polygon is to enable the multichain Ethereum ecosystem. It provides a network that offers interoperability between previous and present infrastructure scenarios of Ethereum. Due to this, it offers great functionality and the fastest transaction speed of almost 65,000 transactions per second.
IPFS
IPFS or InterPlanetary File System is simply a distributed system for storing and accessing files, websites, applications, and data. In order to find content IPFS uses content addressing to identify it rather than its location. By contrast, every piece of content that uses the IPFS protocol has a content identifier or CID, that is its hash.
Smart Contract
A smart contract is a computer program or a transaction protocol that is intended to automatically execute, control, or document legally relevant events and actions according to the terms of a contract or an agreement.
Make NFT Collection with Smart contract in one placeDeFi
Defi stands for Decentralized Finance, a blockchain-based form of finance that does not rely on central financial intermediaries like banks or financial institutions to offer services or products, instead of that it uses smart contracts* on blockchains.
With DeFi, you not only have control and visibility over your money but also have exposure to global markets and alternatives to your local currency or banking options
Metaverse
it’s simply a virtual-reality space in which users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other users.
In other terms 'metaverse' is a portmanteau that combines the words 'meta' and 'universe. ' It is used primarily to refer to an anticipated future iteration of the internet that's often hailed as Web 3.0.
Crypto wallet A cryptocurrency wallet is an application that functions as a wallet for your cryptocurrency. It is called a wallet because it is used similarly to a wallet you put cash and cards in. Instead of holding these physical items, it stores the passkeys you use to sign for your cryptocurrency transactions and provides the interface that lets you access your crypto.
Remember:
- A cryptocurrency wallet is a device or program that stores your cryptocurrency keys and allows you to access your coins.
- Wallets contain a public key (the wallet address) and your private keys needed to sign cryptocurrency transactions. Anyone who knows the private key can control the coins associated with that address.
- There are several different types of wallets, each with its own features and levels of security.
- Many cryptocurrency wallets can be used to store keys for different cryptocurrencies.
Wallet address
A wallet address is similar to a bank account number - with a few differences. If you want to receive crypto from someone else, you'll give them your wallet address so they know where to send it. And, unlike a bank account, one wallet can have multiple receiving addresses generated by its public key.
Peer-to-peer
relating to, using, or being a network by which computers operated by individuals can share information and resources directly without relying on a dedicated central server, In peer-to-peer computing, every client can be a server.
Token standards
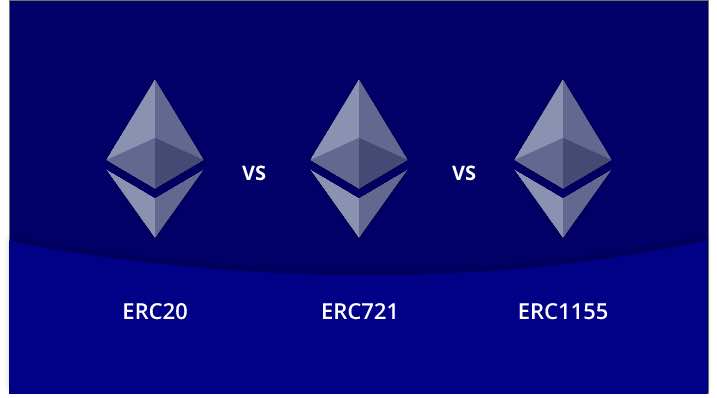
ERC token standards explain certain rules for all the ERC tokens built on the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum’s community duly reviews this set of rules, and amendments are done based on the changing requirements. Moreover, ERC standards are designed to allow ERC tokens to interact seamlessly.
ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155 appear as the three popular ERC token standards or protocols that have their applications across major industries.
Difference between ERC20-ERC 721-ERC 1155: The ERC 721 and ERC 20 are perfect for releasing individual non-fungible and fungible tokens, respectively. Whereas, the ERC 1155 standard is perfect for releasing several tokens at the same time, along with the ability to add fungible and non-fungible tokens in it.
Airdrops
An airdrop is an unsolicited distribution of a cryptocurrency token or coin, usually for free, to numerous wallet addresses. Crypto airdrops are profitable because they give you free tokens that you can sell and make money. However, there are scam airdrops aimed at stealing your funds and leaving you with worthless coins.
OpenSea
OpenSea is the leading marketplace for non-fungible tokens. The platform lets users buy and sell NFTs on the secondary marketplace and also create their own NFT collections to sell on the primary marketplace. The OpenSea marketplace is easy to navigate, with a filter feature to help you find the NFTs you need.
DAO:
A DAO, or “Decentralized Autonomous Organization,” is a community-led entity with no central authority. It is fully autonomous and transparent: smart contracts lay the foundational rules, execute the agreed-upon decisions, and at any point, proposals, voting, and even the very code itself can be publicly audited.
Gas fees: A gas fee is an amount of Ether (ETH) required for an Ethereum blockchain network user to conduct a transaction on the network. Gas fees are used to compensate Ethereum miners for their work in verifying transactions and securing the network.
Minting NFTs: “Minting” an NFT is, in more simple terms, uniquely publishing your token on the blockchain to make it purchasable.
When you decide to create an NFT, you must first “mint” the digital version of your artwork. Minting an artwork refers to the act of tokenizing the artwork, i.e. uploading it to a given marketplace platform (SuperRare, Nifty Gateway, Makersplace, Foundation…) and issuing a token to guarantee its authenticity.
Collection, Collectibles: NFT Collection Means a collection or a series of NFTS. While Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are digital assets having distinct characteristics. A particular asset may have any number of different NFTs
Rarity: NFT rarity determines how rare and valuable an NFT is. Collectors highly prize truly rare NFTs, which makes them more expensive. Consequently, people want to know whether the NFT they own is rare or whether the one they plan to purchase is rare.
What are NFTs?
In this part of the guide, we will break down what are NFTs.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are unique digital items with blockchain-managed ownership. There are many kinds and applications of NFTs - but before we dive into the details, let's learn about a key term: fungibility.

Fungible Items?
If something is fungible, it is easily exchanged with something of equal value. Don't get overwhelmed by the idea of fungibility; it's just the ability of a good or item to be interchanged with other individual goods or items of the same type.
A fungible item is one that can be replaced by an identical item. Think of a dollar bill. My $1 bill has the same purchasing power as your $1 bill and any other $1 bill in circulation. In other words, they’re mutually interchangeable.
Non-Fungible Items:
A non-fungible item, on the other hand, is unique and can’t be copied or substituted. The Statue of Liberty, the Mona Lisa, and a ticket for a seat at the Super Bowl are all non-fungible items. That is to say, they’re one-of-a-kind.
In the crypto world, if I hold one Ethereum token (ETH), it’s fungible because it’s worth the same as any other ETH token someone else is holding. On the other hand, I currently own a Crypto Coven, a profile picture NFT project featuring drawings of witches with individual lore written for each one. Mine, named soursop the cloudless (pictured below), is a non-fungible token (NFT) because out of all the 9,757 total Crypto Coven NFTs in existence, there’s only one that looks exactly like mine.
Types of NFTs:
There are two types of popular NFTs.
- 1/1 NFTs - known as ERC-721 tokens on Ethereum and Polygon, KIP17 on the Klatyn blockchain.
- Semi-fungible NFTs - known as ERC-1155 tokens on Ethereum and Polygon, KIP37 on Klatyn.
1/1 NFTs, known by their token standard as ERC-721 on Ethereum, are the classic definition of Non-Fungible Tokens that we've described above. Each NFT is unique and distinct from other NFTs.
Semi-fungible NFTs, known by their token standard ERC-1155 on Ethereum, are slightly different. Because they are semi-fungible, the items themselves are distinct from other NFTs. However, they might have a quantity greater than one. These NFTs are great for gaming items and creating membership passes for your community! If you want to create your own semi-fungible NFT, we recommend creating them on Polygon.
History of NFTs: How NFTs start?
Some people thought that NFTs began in 2017, But what they don’t know is that NFTs really started in 2012 with the Colored coins and got developed over the years to become what we know now.
2012-2013: Beginning of NFTs with colored coins
The idea of NFTs emerged from what is called a “colored coin”, initially issued on the Bitcoin blockchain in 2012-2013. Colored coins are tokens that represent real-world assets on the blockchain and can be used to prove ownership of any asset, from precious metals to cars to real estate, even equities, and bonds. Although not as sophisticated, this original idea was to use the Bitcoin blockchain for assets like digital collectibles, coupons, property, company shares, and more. They were described as new technology and gave raw possibilities for the future prospects of utilization.
2014-1015: Counterparty & Spells of genesis
In 2014 Robert Dermody, Adam Krellenstein, and Evan Wagner founded Counterparty, a peer-to-peer financial platform and distributed, open-source Internet protocol built on the Bitcoin blockchain. Counterparty allowed asset creation and had a decentralized exchange, thus providing a way for users to create their own tradable currencies. It had numerous ideas and opportunities, including meme trading without counterfeit issues.

In April 2015 Counterparty partnered up with the team creators of Spells of Genesis. The Spells of Genesis game creators were not only pioneers for issuing in-game assets onto a blockchain via Counterparty, but they were also among the first to launch an ICO. The creators helped fund the development of Counterparty by introducing their own in-game currency called BitCrystals.
2016: First rare pepes
memes started to make their way onto the Counterparty platform. People started to add assets to a particular meme called “Rare Pepes.” Rare Pepes are a meme featuring an interesting frog character that has acquired an intense fanbase over the years. What started out to be a comic character named Pepe the Frog, has now steadily become an internet sensation as one of the most popular memes.

2017: Crypto Arts & Cryptopunks
By early 2017, with Ethereum gaining prominence, Rare Pepes started to be traded there as well. CryptoArt was born with the Rare Pepe Wallet and it was the first time creators around the world could submit and sell their own artwork. It was also the first time digital art could have intrinsic value.
As Rare Pepes trading picked up, John Watkinson and Matt Hall, the creators of Larva Labs, created unique characters generated on the Ethereum blockchain. No two characters would be the same and they would be limited to 10,000. The project name, Cryptopunks, was referenced to an experiment with Bitcoin in the 1990s and can be described as an ERC721 and ERC20 hybrid.

Shortly after the release of CryptoCats, Axion Labs introduced CryptoKitties. Those tokens were unveiled in October 2017 and became the next NFT phenomenon to hit the market.
The collection officially launched the following month in conjunction with Dapper Labs and included a novel breeding feature that allowed holders to generate entirely new CryptoKitty NFTs.
By using a genetic algorithm, holders can breed (combine) any two NFTs to produce offspring with their own set of unique traits, determined by the immutable genotypes stored in the smart contract.
2018-2020: New opportunities & Marketplaces
New NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, SuperRare, and KnownOrigin were launched, and NFTs could be created on platforms like Mintable and Mintbase.
NFT marketplaces developed. Existing NFT marketplaces were updated and new platforms like Rarible and Cargo were released. Before 2020, NFT creators had to program smart contracts themselves if they wanted to add features like bulk creation and unlockable content to their NFTs. New platforms meant these features were now readily available during the NFT minting process.
2021: NFTS explosion
2021 was the year NFTs exploded. Celebrities and established brands became interested in NFTs and NFT art gained mainstream popularity. Beeple’s “Everyday: the First 5000 Days” sold for $69.3 million at Christie’s art auction, only to be topped by the $91.8 million sales of Pak’s “The Merge” in early December.
Pak’s NFT was sold to more than 28,000 users who bought over 260,000 shares in his artwork – valuable proof of fractional ownership.
The first-ever Twitter post was sold as an NFT for $2.9 million in 2021. Over the year, CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club NFTs routinely sold for hundreds of thousands of dollars and yesterday’s memes were re-sold as today’s NFTs. Songs, albums, and books were released as NFTs. Meanwhile, experts continue to develop new uses for NFTs outside of the creative industries.
TOP 5 NFTs Projects:
Every day a lot of NFTs projects and collections are minted on opensea or other marketplaces, some of those NFTs are on Ethereum Blockchain, others on Polygon, Solana, or other networks, in this part, we will mention some of the most popular NFTs projects:
Make Your own NFT Collection todayBored Ape Yacht Club By Yoga Labs
Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC), often colloquially called Bored Ape, is a non-fungible token (NFT) collection built on the Ethereum blockchain. The collection features profile pictures of cartoon apes that are procedurally generated by an algorithm.

The parent company of Bored Ape Yacht Club is Yuga Labs. The project launched with a live pre-sale on April 23, 2021. Owners of a Bored Ape NFT are granted access to a private online club, exclusive in-person events, and intellectual property rights for the image.
As of 2022, sales of the Bored Ape Yacht Club NFTs have totaled over US$1 billion. Various celebrities have purchased these non-fungible tokens, including singer Justin Bieber, television host Jimmy Fallon, rapper Snoop Dogg, singer Madonna, Neymar, Paris Hilton, Tom Brady, and DJ Steve Aoki.
CryptoKitties By Dapper Labs

CryptoKitties is a blockchain game on Ethereum developed by Canadian studio Dapper Labs that allows players to purchase, collect, breed, and sell virtual cats. It is one of the earliest attempts to deploy blockchain technology for recreation and leisure. The game's popularity in December 2017 congested the Ethereum network, causing it to reach an all-time high in the number of transactions and slowing it down significantly
CrypotPunks By Larva Labs and now owned By Yoga Labs

CryptoPunks is a non-fungible token (NFT) collection on the Ethereum blockchain. The project was launched in June 2017 by the Larva Labs studio,[1] a two-person team consisting of Canadian software developers Matt Hall and John Watkinson. The experimental project was inspired by the London punk scenes, the cyberpunk movement,[2] and electronic music artists Daft Punk. The crypto art blockchain project was an inspiration for the ERC-721 standard for NFTs and the modern crypto art movement, which has since become a part of the cryptocurrency and decentralized finance ecosystems on multiple blockchains.
CryptoPunks are commonly credited with starting the NFT craze of 2021, There are 10,000 CryptoPunk tokens in both the V1 and V2 contracts. Due to their rarity and exclusivity, they sell for higher prices on the open market and have sold using auction houses like Christie's.On March 2, 2022, an anonymous user donated CryptoPunk #5364 to Ukraine's government Ethereum wallet public address to help fund the Ukrainian government against the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
On March 11, 2022, it was announced that all of the CryptoPunks IP was acquired by Yuga Labs (parent company and creators of the Bored Ape Yacht Club project) for an undisclosed sum. Immediately, Yuga Labs announced they were giving full commercial rights to CryptoPunks owners. On 7th May 2022, the transfer is completed, and the whole CryptoPunks marketplace is moved to the new Yuga Labs-owned website
Start GeneratingDecentraland:

Decentraland is a 3D virtual world browser-based platform. Users may buy virtual plots of land on the platform as NFTs via the MANA cryptocurrency, which uses the Ethereum blockchain.[4] It was opened to the public in February 2020 and is overseen by the nonprofit Decentraland Foundation.
In late 2021 and early 2022, major brands appeared in Decentraland or bought "properties" in it. These include Samsung, Adidas, Atari, PricewaterhouseCoopers, and Miller Lite, and Sotheby's held its first metaverse auction, and in March 2022, Decentraland hosted Metaverse Fashion Week in which major fashion brands appeared, including Dolce & Gabbana, Tommy Hilfiger, Elie Saab, Nicholas Kirkwood, Perry Ellis, Imitation of Christ, and Estée Lauder. Music artists including Deadmau5 and Grimes held concerts on the platform.
CLONE X - X TAKASHI MURAKAMI: By RTFKT
Clone X NFT is a 20K collection, created by RTFKT & Takashi Murakami on the Ethereum blockchain. Released on 11/18/21, Clone X became exclusively available to those who currently held any other RTFKT NFT. Each qualified NFT you held allowed you to mint up to 2 Clone X avatars for only .05 ETH. After the pre-sale concluded, they attempted a Dutch auction starting at 3ETH. However, after the attacks, they ended up with a flat mint price of 2 ETH and quickly sold out.
Clone X and its creators aim to transfer all human consciousness into advanced clone forms and have them create the ultimate Metaverse. In their Metaverse, humans no longer reside in organic form, but rather, are represented by their digital Clone X avatar.
How NFTs Can be used in the real world?

For brand marketing
In an increasingly digital world, there always comes new ways to bring your brand to the awareness of prospective customers. By leaning into what consumers are already opting into in their digital lives, brands can draw attention to their business, communicate their identity and show their commitment to social good.
By projecting themselves as valuable assets to their community, companies can attract customers looking to support purpose-driven brands.
A new way to foster brand loyalty
Tokens are more trendy and brag-worthy than traditional discount codes. Therefore, brands can use NFTs for reinforcing loyalty by giving incentives to token holders. Businesses could develop unique experiences for customers who hold their NFTs. The sort of customers would be those who enjoy exclusivity for a service business.
Privileges given to NFT holders could be priority treatment for product business; it could be access to preorder limited-edition releases, access to the new collection before they get released publicly, or having exclusive releases for NFT holders.
This can also be done by offering holders loyalty rewards and gifts in form of collectibles or marches periodically, seasonally, or occasionally.
Fractional ownership of tokenized assets.
A benefit of putting stakeholding on the blockchain as tokens is that splitting NFTs into individual shares could enable more people to get exposure to blue chips and the opportunity to become part-owners of collectibles or assets they otherwise couldn’t afford. This could be a boost to brands that offer such investment opportunities as a lot more people will get on their NFT train if they find something cheap or affordable.
Allowing investors to split ownership rights of real-world assets like art or Real estate comes with an added advantage if their skates are in form of NFT as NFTs will let individuals effectively manage their stake or ownership as they desire.
Product or goods authentication/recording information about a product (NFT certificate)
NFTs can be used to store information about a physical product on the blockchain. Such NFTs can be programmed to carry the product’s entire history by updating itself whenever the product suffers damage. This is essential for a product with resale value like cars as it will give new buyers authentic and up-to-date information on the car’s history.
Also, companies could use NFTs as a digital seal of authenticity to certify the veracity of a product, by giving buyers of their physical product a digitized version. The digital equivalent of a product will have a cryptographic token assigned to it. token ownership is passed along with the physical product after a customer buys it.
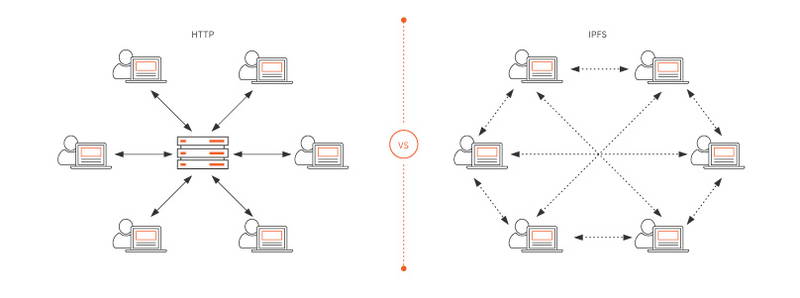
What is IPFS?

IPFS, which stands for InterPlanetary File System, is a communication protocol that uses peer-to-peer networking to store, retrieve, and share data through a distributed file system mechanism.
IPFS is a decentralized, peer-to-peer file-sharing protocol. The IPFS network runs on the web and uses content-addressed storage (CAS) to store data and retrieve it based on its content, not its location. IPFS uses this method to uniquely identify and fetch the data in question.
Using IPFS to store archival data enables deduplication, clustered persistence, and high performance on the posterity of the data.
Generate NFTs andupload to IPFS
How does IPFS work?
When you upload data to an existing node on the protocol, the data is chopped into smaller chunks itself, then hashed and given a unique content identifier (CID), which serves as a fingerprint. This makes it faster and easier to store the small pieces of your data on the network quickly.
Once the data is uploaded to the network, other nodes within the network update their nodes to contain a cached copy of the data. This way, they can also provide the data just like the initial node. It’s up to a node to keep and still provide this data or discard it, for example, as a way to save memory.
For every new upload of new data or previously uploaded data, a new cryptographic hash (CID) is generated, making every upload to the network unique and resistant to security breaches or tampering.
IPFS uses a decentralized naming system to find the name of the file — that’s the long CID string — then maps the CID to a more human-readable DNS name using DNSLink.
IPFS is available for anyone, not just blockchain developers, to use. That includes Web 2.0 developers, content creators, service providers, researchers, archivists, and so on. The major benefit to using IPFS, regardless of the use case, is that it provides a decentralized platform to store and work with your data.
How Data is stored in the IPFS?
IPFS is a peer-to-peer (p2p) storage network. Content is accessible through peers located anywhere in the world, who might relay information, store it, or do both. IPFS knows how to find what you ask for using its content address rather than its location.
There are three fundamental principles to understanding IPFS:
- Unique identification via content addressing
- Content linking via directed acyclic graphs (DAGs)
- Content discovery via distributed hash tables (DHTs)
These three principles build upon each other to enable the IPFS ecosystem. Let's start with content addressing and the unique identification of content.
Content addressing
IPFS uses content addressing to identify content by what's in it rather than by where it's located. Looking for an item by content is something you already do all the time. For example, when you look for a book in the library, you often ask for it by the title; that's content addressing because you're asking for what it is. If you were using location addressing to find that book, you'd ask for it by where it is: "I want the book that's on the second floor, first stack, third shelf from the bottom, four books from the left." If someone moved that book, you'd be out of luck!
That problem exists on the internet and on your computer! Right now, content is found by location, such as:
By contrast, every piece of content that uses the IPFS protocol has a content identifier or CID, that is its hash. The hash is unique to the content that it came from, even though it may look short compared to the original content. If hashes are new to you, check out our guide to cryptographic hashing for an introduction.
Many distributed systems use content addressing through hashes as a means for not just identifying content, but also linking it together — everything from the commits that back your code to the blockchains that run cryptocurrencies leverage this strategy. However, the underlying data structures in these systems are not necessarily interoperable.
This is where the Interplanetary Linked Data (IPLD) project (opens new window)comes in. IPLD translates between hash-linked data structures, allowing for the unification of the data across distributed systems. IPLD provides libraries for combining pluggable modules (parsers for each possible type of IPLD node) to resolve a path, selector, or query across many linked nodes, allowing you to explore data regardless of the underlying protocol. IPLD provides a way to translate between content-addressable data structures: "Oh, you use Git-style, no worries, I can follow those links. Oh, you use Ethereum, I got you, I can follow those links too!"
IPFS follows particular data-structure preferences and conventions. The IPFS protocol uses those conventions and IPLD to get from raw content to an IPFS address that uniquely identifies content on the IPFS network.
The next section explores how links between content are embedded within that content address through a DAG data structure.
Directed acyclic graphs (DAGs)
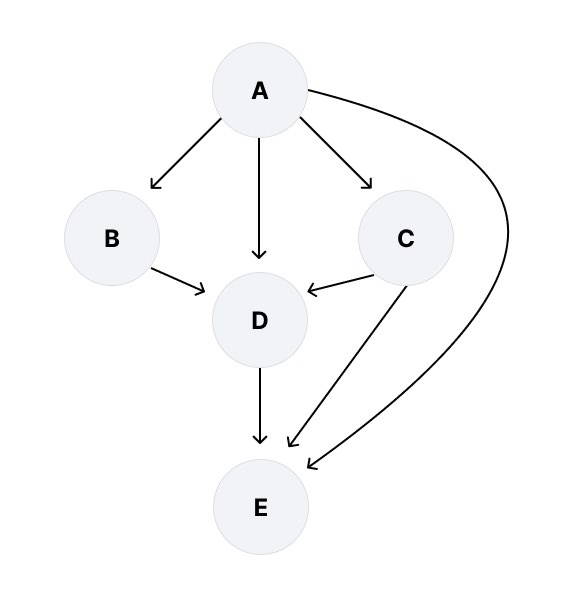
IPFS and many other distributed systems take advantage of a data structure called directed acyclic graphs (opens new window), or DAGs. Specifically, they use Merkle DAGs, where each node has a unique identifier that is a hash of the node's contents. Sound familiar? This refers back to the CID concept that we covered in the previous section. Put another way: identifying a data object (like a Merkle DAG node) by the value of its hash is content addressing. Check out our guide to Merkle DAGs for a more in-depth treatment of this topic.
IPFS uses a Merkle DAG that is optimized for representing directories and files, but you can structure a Merkle DAG in many different ways. For example, Git uses a Merkle DAG that has many versions of your repo inside of it.
To build a Merkle DAG representation of your content, IPFS often first splits it into blocks. Splitting it into blocks means that different parts of the file can come from different sources and be authenticated quickly.
Distributed hash tables (DHTs)
To find which peers are hosting the content you're after (discovery), IPFS uses a distributed hash table or DHT. A hash table is a database of keys to values. A distributed hash table is one where the table is split across all the peers in a distributed network. To find content, you ask these peers.
The libp2p project (opens new window)is the part of the IPFS ecosystem that provides the DHT and handles peers connecting and talking to each other. (Note that, as with IPLD, libp2p can also be used as a tool for other distributed systems, not just IPFS.)
Once you know where your content is (or, more precisely, which peers are storing each of the blocks that make up the content you're after), you use the DHT again to find the current location of those peers (routing). So, to get to the content, use libp2p to query the DHT twice.
You've discovered your content, and you've found the current location(s) of that content. Now, you need to connect to that content and get it (exchange). To request blocks from and send blocks to other peers, IPFS currently uses a module called Bitswap (opens new window). Bitswap allows you to connect to the peer or peers that have the content you want, send them your want list (a list of all the blocks you're interested in), and have them send you the blocks you requested. Once those blocks arrive, you can verify them by hashing their content to get CIDs and compare them to the CIDs that you requested. These CIDs also allow you to deduplicate blocks if needed.
Create NFT Collection Step by Step
Step by step tutorial videoHow to create NFTs collection layers on photoshop:
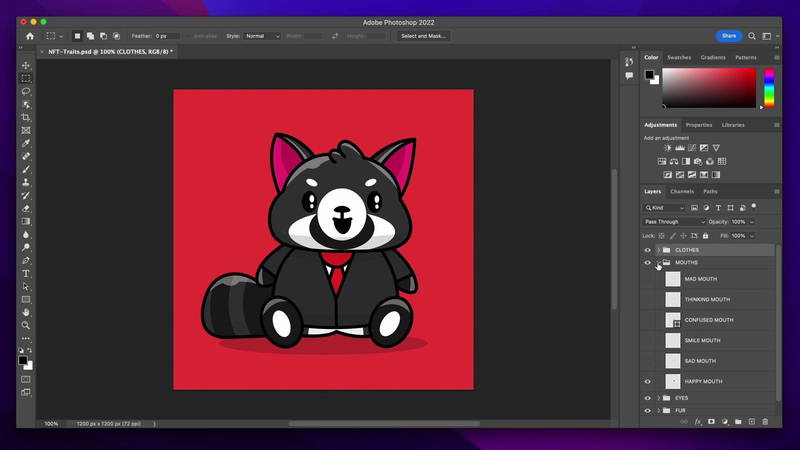
Usually, when you export an image from photoshop, all the layers will fuse. You can not separate them from one another. To generate an NFT collection, you should have NFT layers separated.
First, you have to create your NFT layers with variations. The bottom layer is the background after that base image. On top of the base image, you can have other layers with different styles and variations.
The number of NFTs you can generate using NFT generators depends on the number of layers you created.
For example, let’s assume you have 9 background layers, 1 base layer, 3 different eye layers, 5 mouths, 8 noses, and 10 ears. Then you can calculate the NFT number like this. So you can generate up to 2520 NFTs. (NFTs Number = 9*1*3*5*8*10 = 10800)
Calculate the number of NFTs
Before exporting the layers, ensure visibility is “On” for all the layers. Then click “File” and navigate to the “Export” menu. Then select the “Layers to files”(File > Export > Layers to files). A new popup window will open.
Export Photoshop Transparent PNG Layers
Make sure you choose the correct path to save these layers and other settings. Tick mark “Transparency” and select PNG as the file format. After all, click the “Run” button to start the process. Photoshop takes some time to export all the layers.
You can also export your files as a PSD project.
Rename Layers:
After having your PSD file or your Folder containing your PNG files, you should rename all layers with their Traits or characters to make it easier for you to generate your metadata and properties.
Generate Your NFTs Collection
Now we are ready to generate your NFTs collection from the single images you just created. While this part is definitely the easiest one.
- Go to Genfty.com
- Click on the ‘Make NFTs’ page: you’ll have a full guide to follow or you can just watch the video.
- Upload your PSD file or Add a new group for each of your layers group then upload your traits successively respecting the order of your layers: Background, Base layer, eyes, mouth, nose, and ears.
- Set dimensions for your NFTs.
- Rename your layers and traits to be generated correctly in metadata.
Enable rarity for each layer: (make sure the total of rarities in each group is equal to 100% )
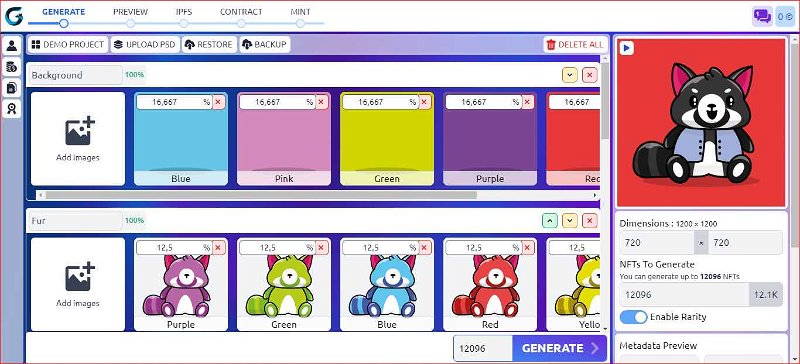
Before generating your NFTs you can back up your project to save all layers with their names and rarity percentages.
Click on Generate to start generating your NFTs collection.
Upload your NFT collection To the IPFS and generate a smart contract
After generating your collection you can either download the NFTs or upload them to the IPFS.
Download your NFTs: Click on the download zip file button, and you’ll find your Collection in your downloads folder.
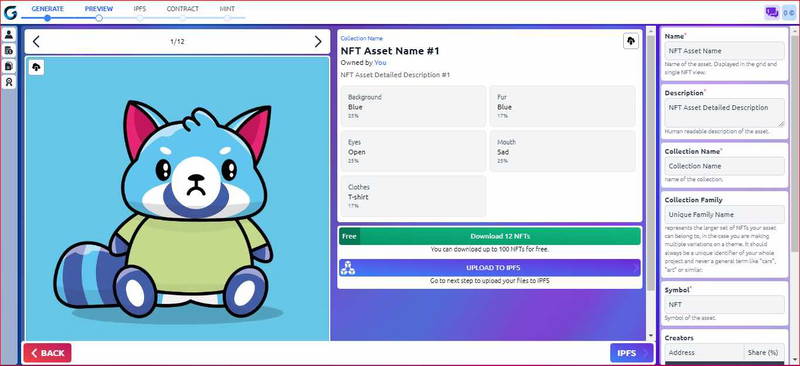
Upload to the IPFS: you’ll need to upload your images (NFTs) and metadata to the IPFS to simplify The mint of your collection.
Before uploading to the IPFS make sure to edit your collection’s information:
name: it referred to the asset name, it’s shown in the grid and single NFT view
Description: you should add a description of your collection and what it’s about.
symbol: Symbol of the Asset, example: WoW is the symbol of the world of women
creators: Public key of each creator. Shown in the single NFT view, resolved to Twitter handles if they are connected via Solana name service.
Seller fee basis points: Royalties percentage awarded to creators. Shown as a percentage received by each co-creator.
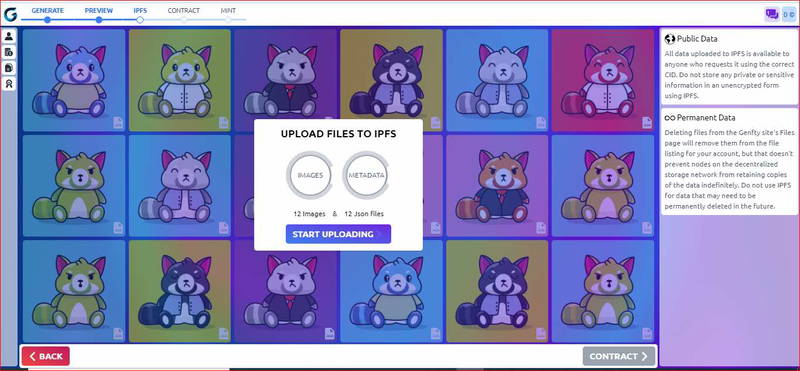
After Uploading to the IPFS you’ll have your CID ( content ID of your NFTs) and the preview link of your images and metadata.
All data uploaded to IPFS is available to anyone who requests it using the correct CID. Do not store any private or sensitive information in an unencrypted form using IPFS.
Permanent Data
Deleting files from the Genfty site's Files page will remove them from the file listing for your account, but that doesn't prevent nodes on the decentralized storage network from retaining copies of the data indefinitely. Do not use IPFS for data that may need to be permanently deleted in the future.
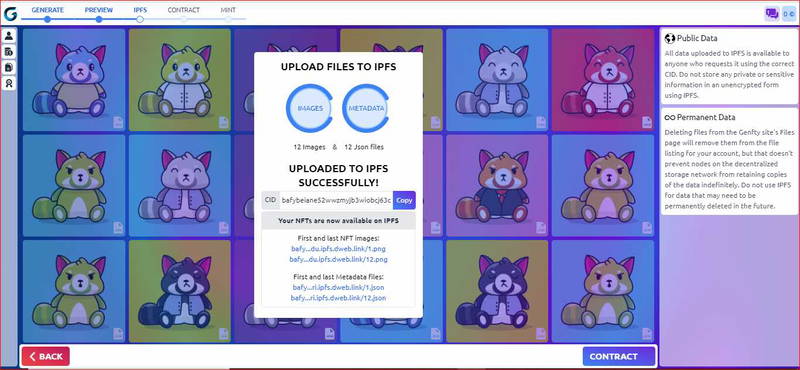
How to Generate Smart contract?
You don’t have to write your smart contract, with Genfty you can Generate a smart contract with no code or programming skills, it’s easy, After uploading your NFTs collection to the IPFS click on the Generate smart contract button: this is the most “professional” option and gives you great control while saving you a lot of time.
What’s next? Mint your NFTs
After completing all the Big steps of generating your NFTs and preparing your smart contract, now you can deploy the smart contract to start minting your NFTs on the marketplace.
All you’ll need in this step is to add and complete some information about your collection and your minting.
Step 1: complete information about your NFTs collection:
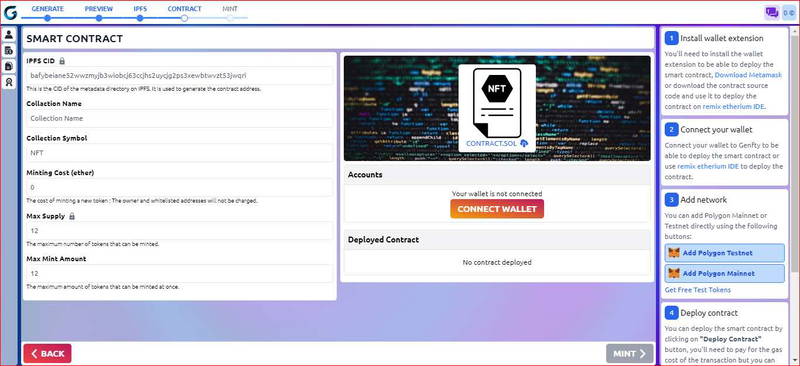
Collection name and symbol: add the name you’ve chosen to your NFTs collection and the symbol.
Minting cost: The cost of minting a new token: The owner and whitelisted addresses will not be charged.
Max supply: The maximum number of tokens that can be minted. it’s generally the same as the number of NFTs in your collection.
Max Mint Amount: The maximum amount of tokens that can be minted at once.
Step 2: Connect your wallet
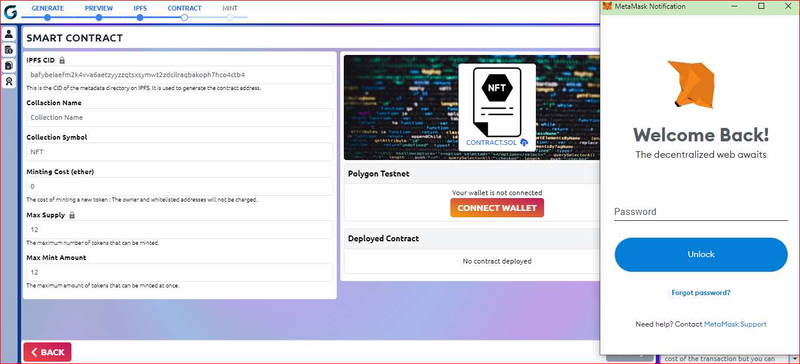
If you already have a crypto wallet, Connect your wallet to Genfty to be able to deploy the smart contract or use remix Ethereum IDE to deploy the contract.
If you don’t have a crypto wallet you can create one using metamask.
You'll need to install the wallet extension to be able to deploy the smart contract, Download Metamask, or download the contract source code and use it to deploy the contract on remix Ethereum IDE.
Step 3: Deploy smart contract
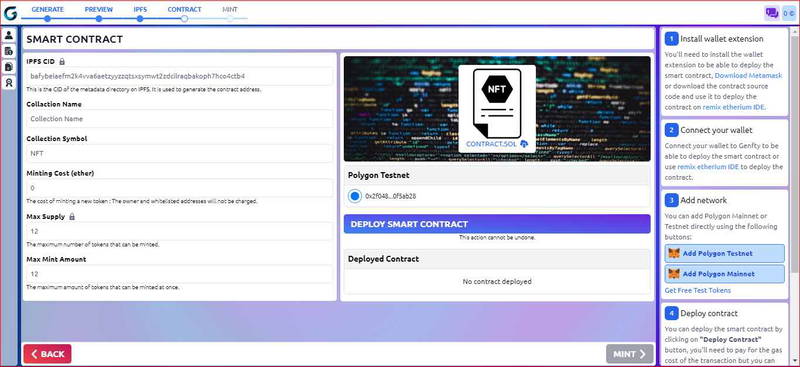
You can deploy the smart contract by clicking on the "Deploy Contract" button, you'll need to pay for the gas cost of the transaction but you can deploy the contract without paying real coins by using testnet network instead of mainnet.
Step 4: Verify and publish the contract
Source code verification provides transparency for users interacting with smart contracts. You can verify & the contract based on the network you are using.
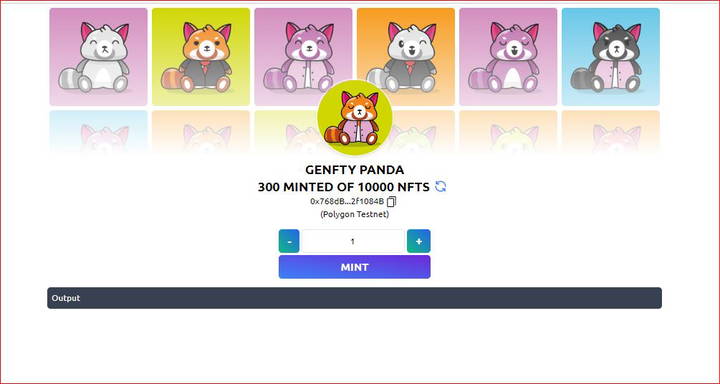
Step 5: Mint NFTs
You can mint your NFTs directly from Genfty.com or you can use your verified smart contract and mint NFTs from etherscan or polygonscan based on the network you use to deploy the smart contract.
All you need is to set the number of NFTs you want to mint and click Mint button and confirm the transaction
Sell NFTs
Where can I sell my NFTs: top Marketplaces to sell NFTs
Now that you’ve generated your own NFTs collection, you’re certainly wondering where can I sell My NFTs.
In this part of the guide, we will be listing some of the best marketplaces where you can sell your NFTs and the properties of each one of them.
OpenSea
OpenSea is ancient by NFT standards, having launched in 2017, and it’s also among the largest NFT marketplaces active today. It hosts many popular NFTs, including art, music, photography, trading cards, and virtual worlds.
The core cryptocurrencies used on OpenSea are Ethereum, Solana, and USDC, and payment options feature other cryptos. Just note that you can’t use fiat currencies like U.S. dollars or euros.
On the bright side, OpenSea is very user-friendly for beginners. You can set up an account for free within minutes and start browsing NFTs immediately, and you can even create NFTs on their platform.
For costs, OpenSea charges a fee equal to 2.5% of every transaction. You must also pay the gas fee for completing NFT transactions with Ethereum. Gas fees are the transaction fees paid to miners.
If you’re looking to avoid the gas fee, you can use Polygon blockchain to sell your NFTs. But you’ll need to ensure that the NFT item of interest displays the Polygon logo.
In short, OpenSea is a solid choice for beginners looking to get started with a straightforward marketplace.
Start GeneratingBinance
Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges, added an NFT marketplace in 2021. The international crypto exchange is one of many other industry players entering the NFT sector.
Binance NFT offers the typical digital assets found on other major platforms: artwork, gaming items, and collectibles.
A major advantage of Binance NFT is that it charges very low fees. The platform only deducts a 1% trading fee. It’s also a user-friendly platform built using similar technology and layouts as their exchange.
As such a large player in the crypto space, Binance also runs on its own blockchain, giving it an added advantage.
Rarible
Rarible is a community-based NFT marketplace that enables users to access a wide range of NFTs to buy and sell. The platform has an optimized user experience interface that allows users to mint and trade NFTs at ease. Rarible is a unique marketplace that supports three various blockchain networks; Ethereum, Flow, and Tezos. This multi-chain feature initiates the users to mint, buy and sell non-fungible tokens from any one of these effective blockchain platforms in the Rarible NFT marketplace.
SuperRare
SuperRare is an NFT marketplace that is based on the Ethereum blockchain. This is an exclusive NFT marketplace that deals only with a selected number of NFT artists. This marketplace is the pioneer of the exclusive NFT artworks with the motive to preserve them in the name of art collection culture. The SuperRare platform is one of the best NFT marketplaces in the digital space. This marketplace platform has a very particular vetting and approval mechanism before the digital art could be listed for sale. SuperRare is driven by creativity among the creators and it ensures that the collectors will get the best out of the NFT collection. This marketplace is not similar to OpenSea, since it is an exclusive platform, the transaction fee is around 15% on primary sales.
NBA Top Shot:
NBA Top Shop is a marketplace where You can buy video clips, play highlights and art for both the NBA and the WNBA. But some of these Moments aren’t cheap. A LeBron James slam dunk video fetched $208,000 in February 2021.
The NBA built and manages this NFT marketplace, and they have exclusive rights to these video clips. Plus, you know you’re dealing with a large, reputable organization.
The NBA Top Shot marketplace is one example of major companies getting on this trend. Others include the DraftKings Marketplace and the Associated Press’ NFT marketplace. Even GameStop plans to launch an NFT marketplace this year.
Users can purchase Moment NFTs with credit/debit cards or select cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash, DAI, or USDC. And of course, fees are added to the purchase price, whether you’re buying that iconic moment with a credit card or cryptocurrency.
Start GeneratingHow to sell Your NFTs?
Pick your Marketplace:
Now that you’ve got everything in place, you need to pick a marketplace where you will create and then list your NFT.
The most popular ones are SuperRare, Rarible or OpenSea. For the sake of this guide, we’ll pick the last one because it’s free to join and has no moderation on the content you can list. That means you don’t have to be approved as an artist to be selling on the platform. But this also means that the marketplace is full of digital sundries nobody’s ever going to buy.
Connect your wallet to OpenSea:
On OpenSea, click on the user icon, then on “My Profile”. On this page, you can choose how to connect your ETH wallet to proceed. If you’re using MetaMask, you can connect it to the platform by selecting “Use a different Wallet” and then clicking on WalletConnect. The procedure is relatively straightforward. Follow the platform’s prompts, then confirm the Wallet Connect operation from your MetaMask app.
Create your NFT on OpenSea:
Once you’ve connected the ETH Wallet to OpenSea, you can go on and create your first NFT. Click on Create in the top menu, and create a collection. Fill in all the information needed, then save. Now you’re ready to start the actual minting process of a new NFT. Click on New Item, load your artwork, and give all the details you want about it. Once you’re ready to pull the trigger, click create.
Congratulation, you’ve successfully created a token!
Sell Your NFTs:
To sell your token on OpenSea, though, you have to open the newly-minted item in your collection and click on the sell button. On the selling page, you will be able to choose the Ethereum tokens you’ll accept as a payment if you want to sell with a fixed price or at an auction, and the royalties you want to receive from the first and subsequent sales.
Step by step tutorial videoNewsletter
Keep up with our latest NFT news, updates and new features.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Contact us
Our team is here to answer all your questions
Feel free to contact us at contact@genfty.com